It has been almost a year since the COVID-19 recession hit the U.S.
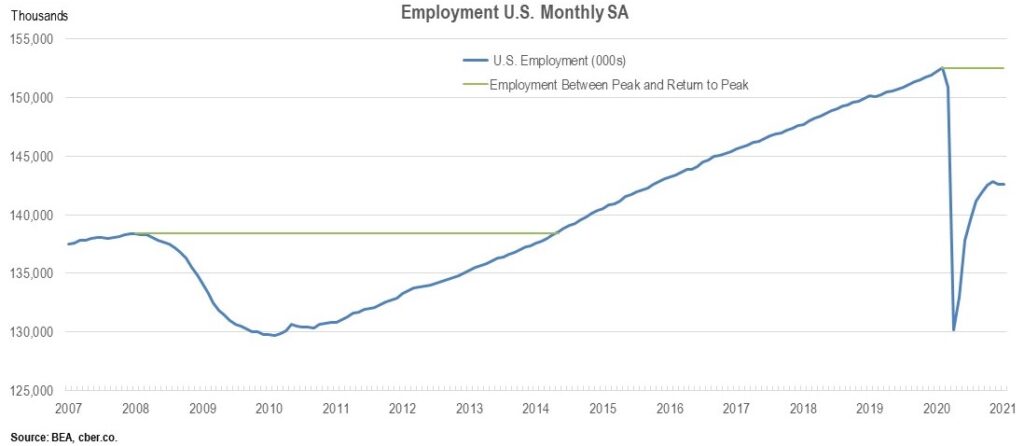
In February 2020, U.S. employment peaked. In March, WHO declared the COVID-19 virus a pandemic. Government leaders put lockdowns in place that caused employment to decline in March and April. At the trough of the decline, in April, U.S. employment was 85.3% of the February 2020 total. Said differently, in March and April, the U.S. economy lost 22.3 million employees.
By the end of 2020, U.S. employment was 93.48% of the February 2020 total. Only 49,000 jobs were added in January 2021. Employment edged up a notch and was 93.51% of the February 2020 total. On a positive note, January employment had increased by 12.4 million jobs.
Through the first part of the summer, the employment recovery was V-shaped. As net job creation tapered off, it has turned into a checkmark shaped recovery.
The Great Recession was much different than the COVID-19 Recession. A shock to the financial system caused the Great Recession. On the other hand, the U.S. financial system was in good shape when policies related to the COVID-19 medical crisis triggered the current recession.
U.S. employment peaked in January 2008. As the financial crisis snowballed, U.S. employment declined for 25 months. This declined was longer than the COVID-19 recession, but not as deep.
At the trough in 2010, U.S. employment was 93.7% of the January 2008 total. It took 51 months of job recovery to return to the January 2008 level. The combined length of the employment decline and recovery was 76 months.
The recovery from the COVID-19 recession will be in Q4 of 2022 or Q1 of 2023. The estimated time of recovery from the trough will be 2.5 to 3.0 years. The total estimated time of recovery from the previous peak is approximately 31 to 37 months.
There are many potential headwinds. Keep your fingers crossed.