The most recent data release by the Bureau of Labor Statistics showed the Colorado economy remains on solid footing.
The unemployment rate dropped from 6.2% a year ago to 4.0% this year. That sharp of a drop produces significant shock within the system, more so than when the change is more gradual.
With that sharp of decline, it becomes difficult to find workers in some occupations. That difficulty will be accentuated by a sense of urgency to find workers. As well, more industries will face upward wage pressures. That is good for workers, but will cut into the bottom line of companies.
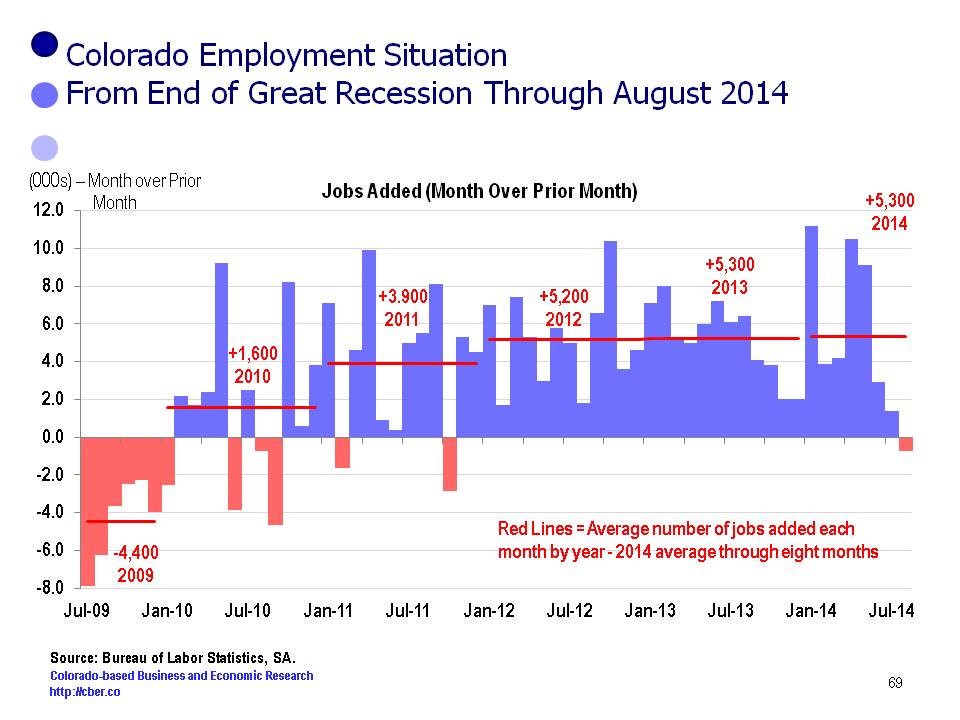
The recent jobs data is another indicator the Colorado economy is continuing to grow at a steady pace. For all practical purposes, it is meaningless to talk about the December numbers. When BLS makes their annual revisions in March, it is likely the number of Colorado jobs will be revised upwards.
The U.S. economy is solid which bodes well for Colorado. New car sales have returned to pre-recession levels, real GDP will be stronger this year both globally and for the U.S., the U.S. should add more than 2.6 million jobs this year (and Colorado should be at least 2.7% of that total), government spending will be stronger, and purchasing managers in manufacturing and service companies are optimistic.
In Colorado, BLS data will show that the number of establishments increased at a greater rate than in 2013. If there are more businesses there are more potential job opportunities for workers.
In 2015 about 60% of job growth will be in construction; health care; accommodations and food services; retail trade; and professional and technical services.
Admittedly, the price of oil will have an effect on the rate of job growth in 2015; however, at a statewide level, most of the top sectors will show steady growth unless the price of oil stays low for an extended period.
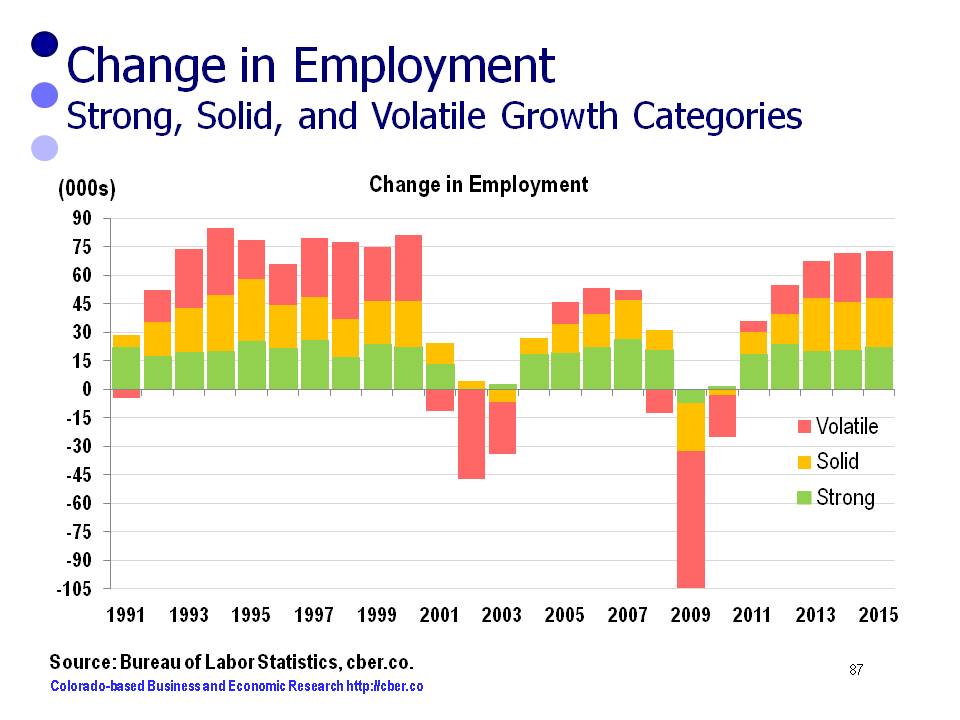
The steady growth that is currently occurring in the Colorado economy is much easier to manage and deal with than the rapid growth the state experienced during the 1990s.