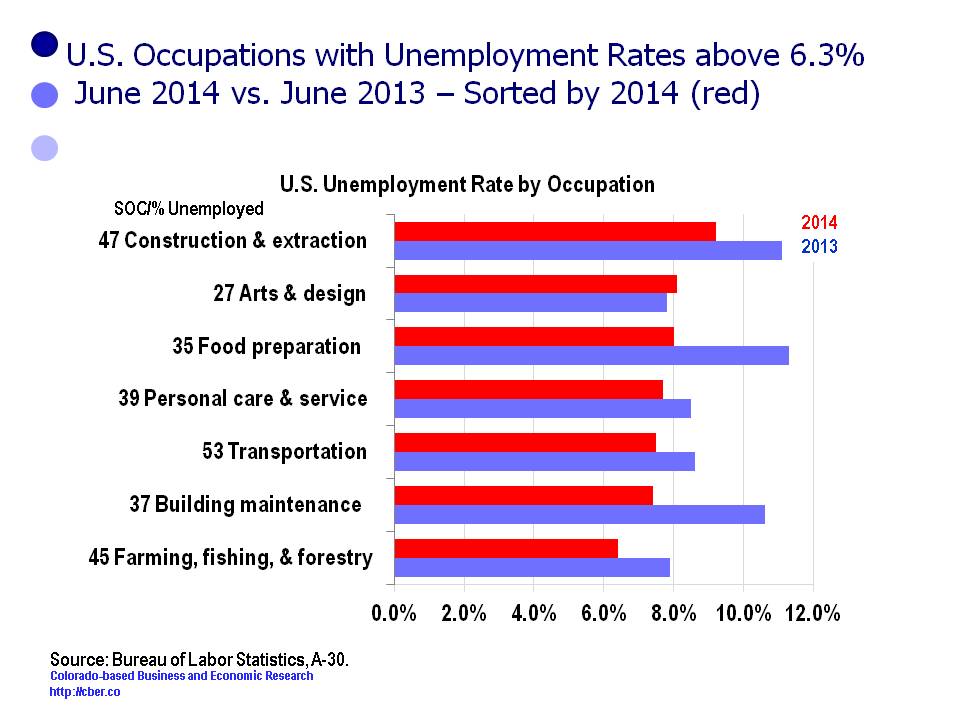
Nationally, the unemployment rate has dropped below 6.0%, to 5.9% and the number of unemployed is now below 9.3 million. While this decline is a positive sign, the number of unemployed remains about 2.5 million above the low point in the second half of 2006.
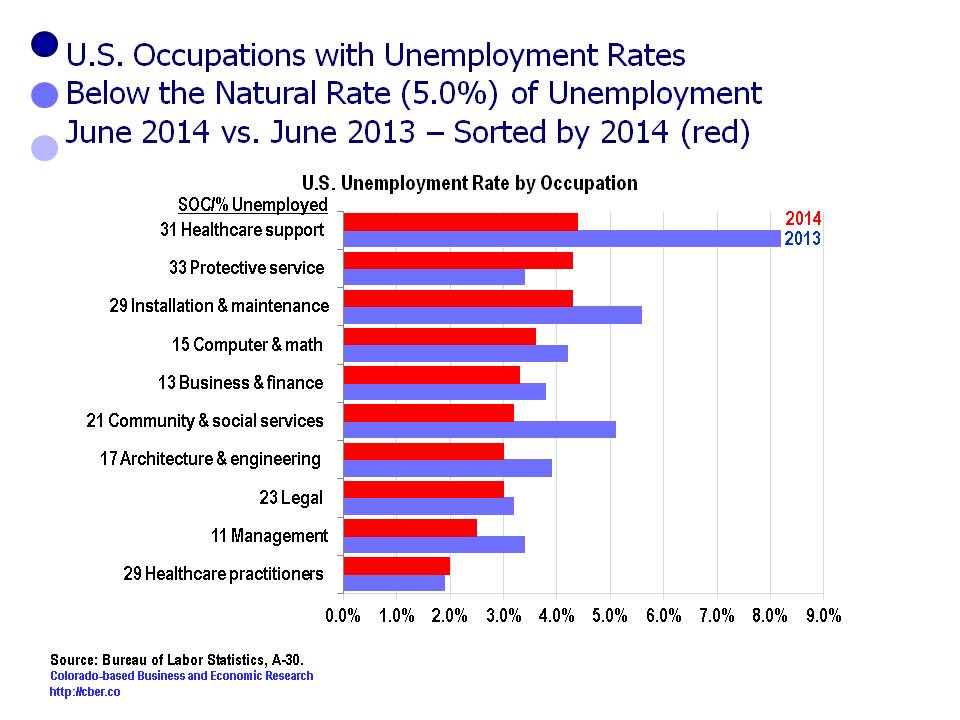
The BLS tracks the unemployment rate in 22 occupations. Ten of those occupations have unemployment rates below the natural rate of unemployment (5.0%).
Most likely there is upward pressure on wages in these occupations at a national level, as well as in Colorado.
| Occupation | Unemployment Rate |
|---|---|
| Legal occupations | 2.2% |
| Management occupations | 2.3% |
| Architecture and engineering occupations | 2.4% |
| Healthcare practitioner and technical occupations | 2.4% |
| Business and financial operations occupations | 2.7% |
| Computer and mathematical occupations | 2.8% |
| Life, physical, and social science occupations | 2.8% |
| Community and social service occupations | 3.3% |
| Education, training, and library occupations, 3.3% | |
| Installation, maintenance, and repair occupations | 3.4% |
| Healthcare support occupations | 4.9% |
Of the above occupations, the ones most critical to Colorado are:
• Architecture and engineering occupations
• Healthcare practitioner and technical occupations
• Computer and mathematical occupations
• Healthcare support occupations
Although the U.S. unemployment rate is approaching the natural rate of unemployment (5.0%), there is limited upward pressure on wages across the nation. This is reflected in the National Association of Business Economists October Survey, which indicated that in Q3 2014, 24% of the respondent firms raised their wages and salaries, about half the percentage that raised their wages in Q2. If there was a potential for upwards wage pressures earlier in the year, those pressures have eased significantly.
The Colorado unemployment rate, 4.7%, and the number of unemployed, 131,348, continues to decline.
Even though the unemployment rate is near the natural rate of unemployment there appears to be minimal upward pressure on wages, except in a few categories of occupations such as specialized high -tech jobs, computer related occupations, and healthcare. In addition, wage pressures may be felt in geographic areas, such as Weld County, where the extractive industries are booming.
In 2009 the average annual wages for all occupations in Colorado, as measure by the QCEW data, was $46,861. By 2013, average annual wages had increased to $50,873, an annualized rate of growth of 2.1%.
Unfortunately, during that same period, the Consumer Price Index for the Denver-Boulder-Greeley area increased at an annualized rate of 2.6%. In other words pay increases did not keep up with increases in the cost of living. This year inflation is projected to increase at a higher rate than the gain in total wages.
On average, Colorado employment is 65,200 greater for the first 9 months of 2014 than the same period in 2013. That total will likely be revised upwards when the BLS benchmarks the CES data series in March 2015.
Looking ahead for the remainder of the year, the tourism; construction; health care; and professional, scientific, and technical services sectors will continue to be the primary sources of growth. Although, the extractive industries are small they are the source of greater indirect job growth and significant output growth.