After ten months, enough of the year has passed that Colorado’s employment situation for 2014 is virtually set. This post looks at overall and regional job growth, drivers of the regional economies, and industries that dominate state job growth.
Job Growth (Overall)
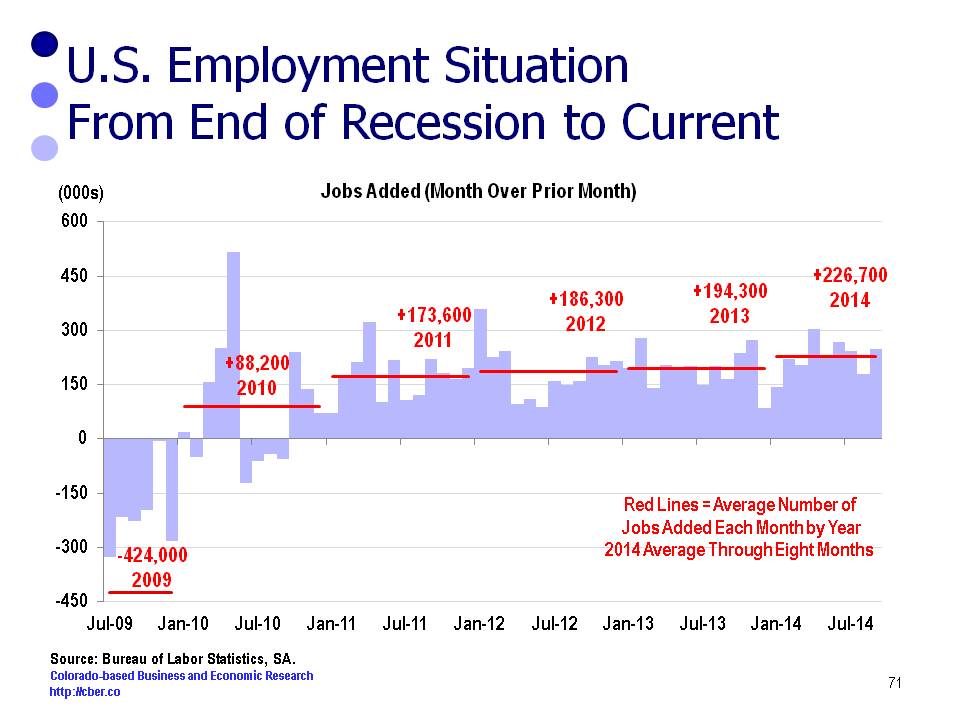
After BLS makes their March 2015 revisions the wage and salary employment will show that Colorado added at least 70,000 jobs this year. That is job growth of at least 2.9%.
Job Growth (Regional)
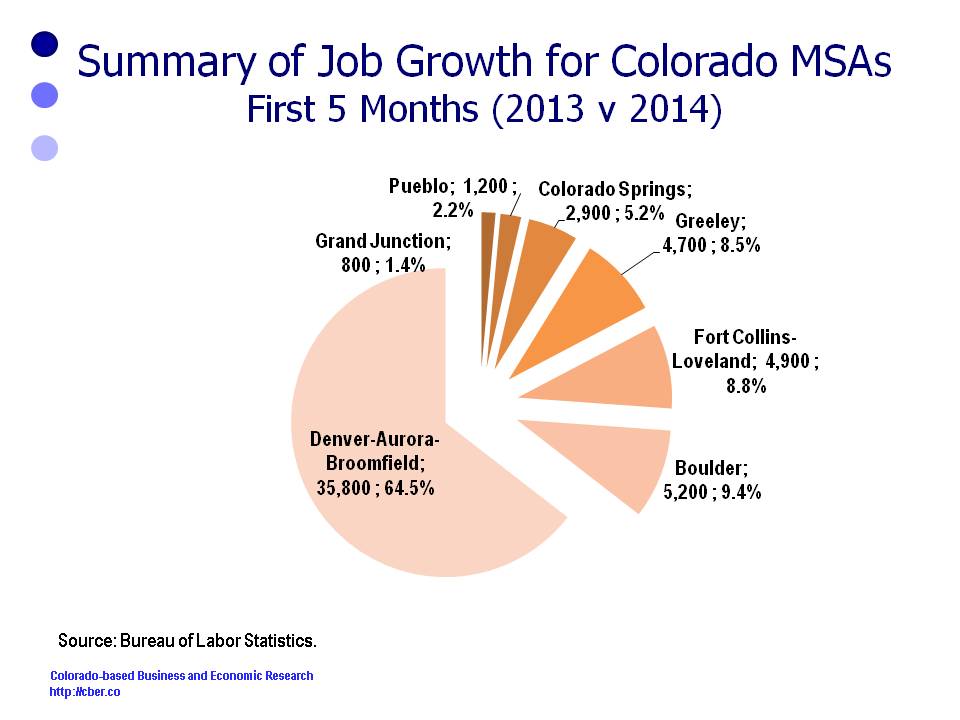
About 81% of Colorado’s job growth occurs in Colorado’s seven metro areas (listed below). The industry composition and the economies in these seven metro areas are distinct. As a result they have grown at different rates.
The estimated rates of job growth through ten months are:
• Greeley 5.0%
• Boulder 3.1%
• Fort Collins 2.8%
• Denver 2.8%
• Pueblo 1.8%
• Grand Junction 0.9%
• Colorado Springs 0.8%
During this period the percentage of job growth in the MSAs was:
• Denver added 67.4% of the MSA jobs.
• Boulder added 10.0%.
• Combined, the Northern Colorado MSAs added 16.0% of all jobs (Greeley 8.5% and Fort Collins 7.5%).
• Colorado Springs added 3.6% of the MSA jobs.
• Pueblo added 2.1%.
• Grand Junction added almost 1%.
Drivers of Regional Economies
The economies of Colorado’s seven metro areas are very distinct as evidenced by the industries driving their economy.
• Greeley has been driven by the extractive industries and Vestas.
• Fort Collins has been driven by the high-tech industry, CSU, and spillover from the extractive industries.
• Boulder has posted gains as a result of the high-tech industry, and CU employment.
• Denver’s economy is more balanced than the smaller economies. Interestingly enough, it has grown at a slower rate in 2014 than 2013.
• Pueblo has benefitted from Vestas.
• Grand Junction has struggled to recover from the most recent “oil shale bust”.
• Colorado Springs is still feeling the pain from the exit of Intel. In addition, the wildfires during the summers of 2012 and 2013 played havoc with the economy. The local economy is very dependent on the military and defense funding for local businesses. These industries are typically more volatile than the overall economy.
Industries Dominating State Job Growth
• Throughout 2014, job growth across the state has been led by the following sectors
o Accommodations and Food Services (AFS)
o Health Care
o Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services (PST)
o Construction
o Retail
These five sectors account for about 71% of total job growth in the state.