Both Boulder County and Larimer County are the source of innovation and entrepreneurship that helps drive the Colorado economy.
This analysis compares changes in the unemployment rate, population growth, the number of private sector establishments, and employment. It shows how the growth patterns for the two counties are significantly different for these demographics.
In summary, this comparison shows that:
• Since 2001, Boulder County and Larimer County have usually had unemployment rates below the state – which is a mixed blessing.
• Since 2001, the population, employment, and number of private sector establishments for Boulder County have grown below the rates for Colorado and Larimer County.
Finally, this analysis poses questions that relate to the changes in these data sets.
Unemployment Rate
Typically, the unemployment rates for both Boulder and Larimer County are below the rate for the state.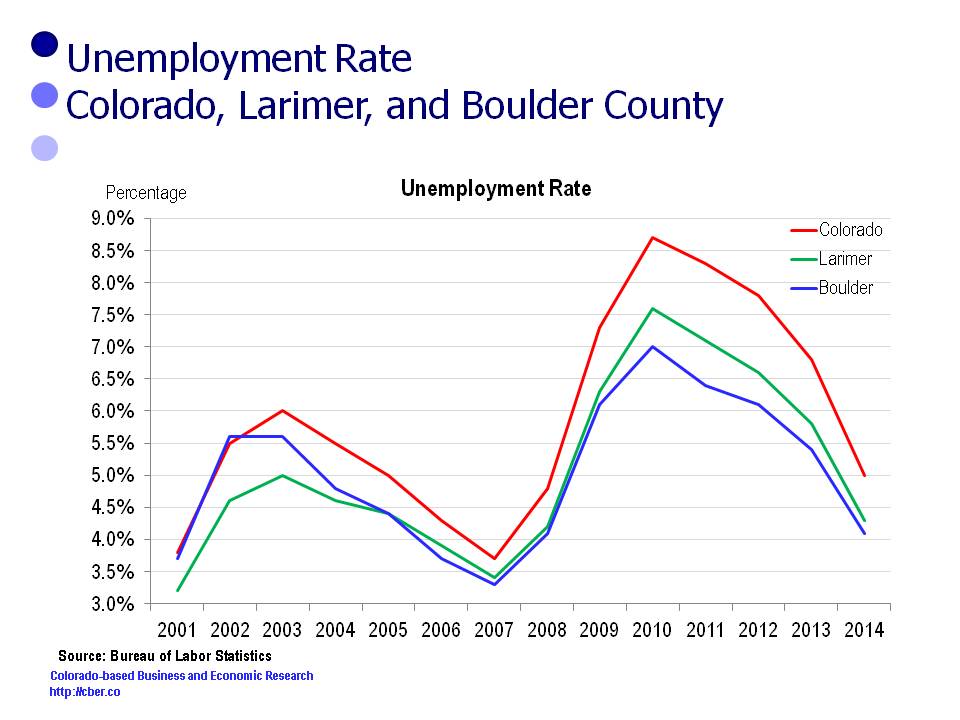
Population
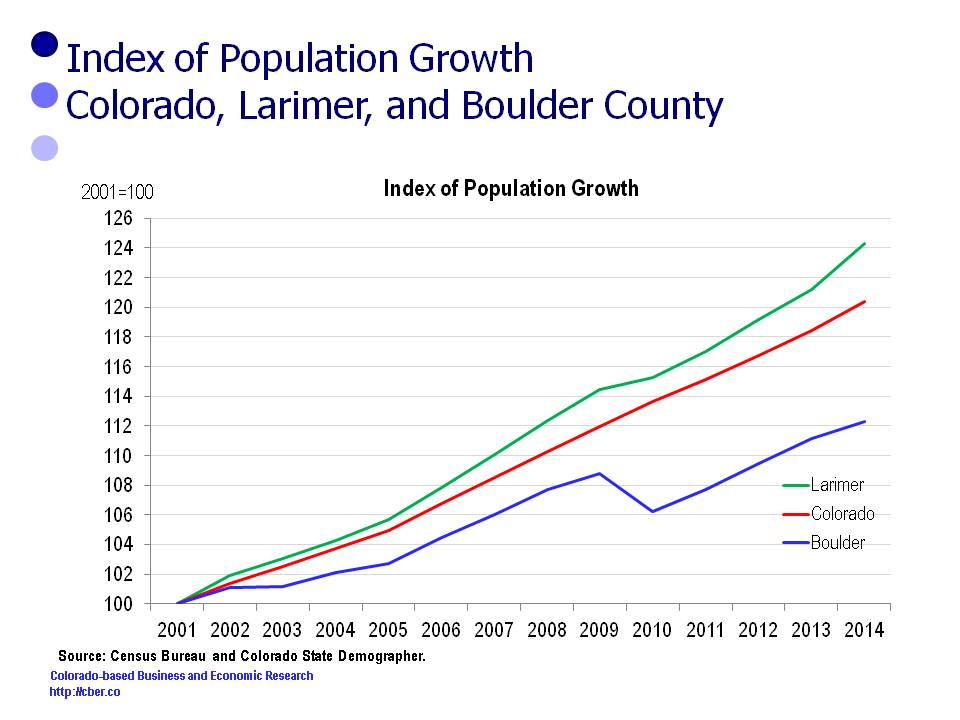
In 2001 Larimer County population was 260,746. It increased by 63,376 and was 324,122 in 2014.
In 2001 the Colorado population was 4,444,513. It increased by 906,059 and was 5,350,572 in 2014.
In 2001 Boulder County population was 278,981. It increased by 34,352 and was 313,333 in 2014.
For this period the rates of change in the population follow:
• Larimer County 24.3%
• Colorado 20.4%
• Boulder County 12.3%.
Establishments
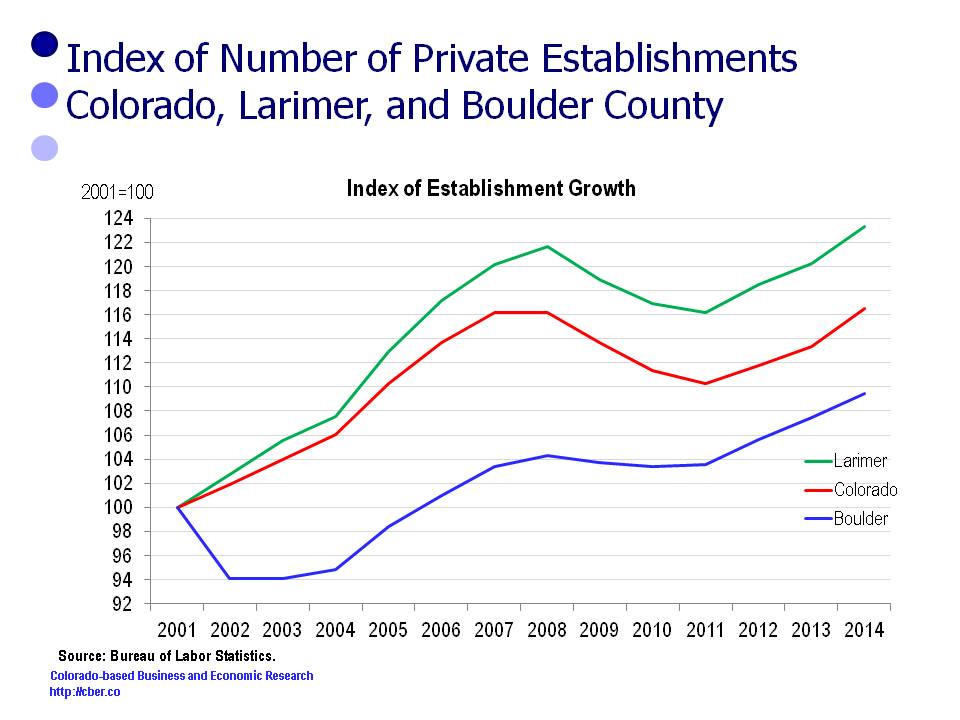
In 2001 there were 8,479 Larimer County establishments. The number increased by 1,976 to 10,455 in 2014.
In 2001 there were 151,025 Colorado establishments. The number increased by 24,957 to 175,992 in 2014.
In 2001 there were 12,335 Boulder County establishments. The number increased by 1,165 to 13,500 in 2014.
For this period the rate of change in the number of establishments follows:
• Larimer County 23.0%
• Colorado 16.5%
• Boulder County 9.4%.
Employment
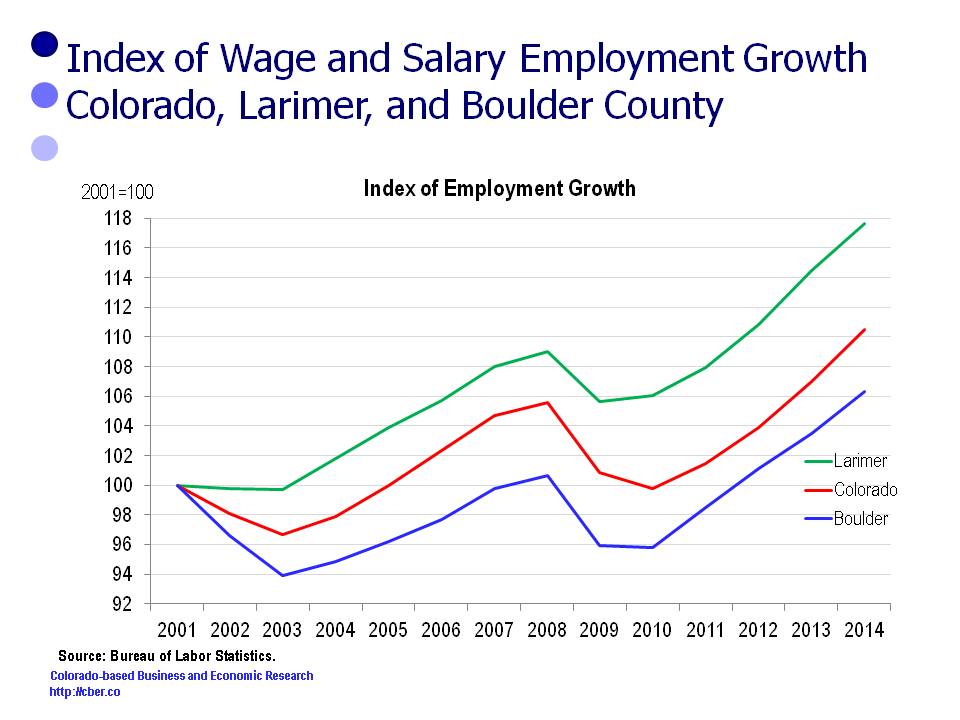
In 2001 Larimer County employment was 126,300. It increased by 22,300 and was 148,600 in 2014.
In 2001 Colorado employment was 2,226,800. It increased by 234,000 and was 2,460,800 in 2014.
In 2001 Boulder County employment was 166,200. It increased by 10,500 and was 176,700 in 2014.
For this period the rate of change in the employment follows:
• Larimer County 17.6%
• Colorado 10.5%
• Boulder County 6.3%.
Implications
The following questions arise when looking at the changes in the unemployment rate, population, the number of private sector establishments, and employment in Boulder County and Larimer County. (Boulder County is also the Boulder MSA and Larimer County is the Fort Collins MSA).
• How do organizations in Boulder and Fort Collins find qualified workers when the regional unemployment rate is lower than the state and other MSAs? Do they have established training programs? Do they recruit workers from other companies (in-state or out-of-state)? Do they provide their workers premium compensation packages?
• Why is the rate of growth for the Boulder population lower than Fort Collins and the state? Is this a result of a lack of affordable and attainable housing in Boulder? Will the completion of improvements to the 36 corridor make it easier for workers to commute to Boulder? Can commuters afford to use it?
• Why are the number of new business establishments in Boulder growing at a slower rate than Colorado and Fort Collins? Is there a lack of adequate commercial space? Is commercial real estate too expensive in Boulder? Why are other areas more attractive? Is it too expensive to operate a business in Boulder? Is it necessary to export innovative ideas out of Boulder so companies can be successful? Why do companies stay in Boulder
• Why is the employment growth rate for Boulder lower than the state and Fort Collins?
This analysis of data for Larimer, Boulder, and Colorado shows that communities have varied business development policies and priorities that have been successful in different ways.